The Santa Maria di Missione chapel in Villafranca Piemonte, northern Italy, stands at the end of a long cornfield. Behind it, the mountains rise gently, their outlines caressed by the sun. The colours of autumn frame the 15th-century frescoes that embellish the structure’s interior, painted by Italian artist Aimone Duce, of the Lombard school. The chapel is the municipality’s oldest religious building, serving about 4,000 inhabitants, and stands on the site of a pre-existing building dating back to 1037.
Inside the small chapel, my footsteps echo softly against the walls, breaking the stillness of the surrounding countryside. The sharp scent of plaster mingles with the earthy smell of the fields outside, carried in on the wind along with the sweetness of wheat. Light filters through the narrow windows, catching the vivid hues of a fresco that depicts the seven deadly sins – a theme often revisited in medieval iconography.
 View image in fullscreen
View image in fullscreenMy eye is drawn to the back wall, where the Deposition (Christ being taken down from the cross) unfolds above the altar and, higher up, the Annunciation appears in delicate contrast. Together, the frescoes meditate on human nature, its vices, frailty and moral struggle. For this reason, the chapel is regarded as one of the finest examples of the Italian international gothic style.
Santa Maria di Missione is part of an open culture circuit, the Cultura a Porte Aperte, a system created by the Council for Ecclesiastical Cultural Heritage of Piedmont and Valle d’Aosta, and the Fondazione CRT. The goal is to make sacred art accessible through a free app. Once it is downloaded, visitors can book and visit the various churches registered in the system via smartphone, opening the door with a simple QR code near the main entrance.
The churches were almost always closed. Sometimes I would set off to visit them, and the challenge was to find the keyMore than 70 churches and chapels have been made accessible through the project, and on entering them visitors can activate a multimedia narrative system: a story available in three languages, that provides historical and artistic information about the structure, accompanied by music and directional lighting.
“I am particularly struck by the more isolated chapels, located in fields or on the edge of a forest,” says Monsignor Derio Olivero, the bishop of Pinerolo, a small town 25 miles (40km) south-west of Turin. “Many are in meadows or among vineyards – a paradise of silence and beauty. For the faithful in the area, the project offers the chance to find a ‘private chapel’ where they can occasionally take refuge. The same is true for non-believers, who can experience it as a place to nurture their spirituality,” he adds.
 View image in fullscreenThe historic centre of Pinerolo, a municipality in Turin. Photograph: Framarzo/Alamy
View image in fullscreenThe historic centre of Pinerolo, a municipality in Turin. Photograph: Framarzo/AlamyCultura a Porte Aperte allows visitors to explore the churches independently and freely throughout the year. The organisers have arranged the sites into six itineraries in different regions: Langhe and Roero; Monregalese; Colline Torinesi and Monferrato; Pinerolese and Saluzzese; Canavese and Valle d’Aosta-Via Francigena; Val di Susa-Via Francigena. Olivero says that the intention is to extend the project across Italy, with Lombardy already on board. “We are in contact with Lazio. I think about the impact the project could have when there are 700, or even 1,000 churches.”
He explains that the initiative drives regional tourism, attracting local and international visitors. “As a young priest, I was fascinated by small churches; they are rich in 15th-century frescoes, but sometimes abandoned and were almost always closed. Sometimes I would set off to visit them, and the challenge was to find the key, spending hours searching for it.”
These are spaces that promote slow tourism, enabling visitors to discover the area, often through word of mouthWhen I reach the small Piedmontese town of Lusernetta, I find the chapel of San Bernardino da Siena. Built between 1450 and 1520, it is dedicated to Saint Bernardino, who in 1425 travelled to the Lucerne valleys to convert the Waldensians – a proto-Protestantism community known for its strict adherence to the Bible. The simple interior features a series of frescoes by an anonymous painter known as the “maestro di Lusernetta”. But the Madonna of Mercy and Child by Jacopino Longo on the left wall of the nave stands out: the Madonna, sitting on her throne, shelters the family of the Counts of Luserna di Rorà – who commissioned the work – under her blue mantle.
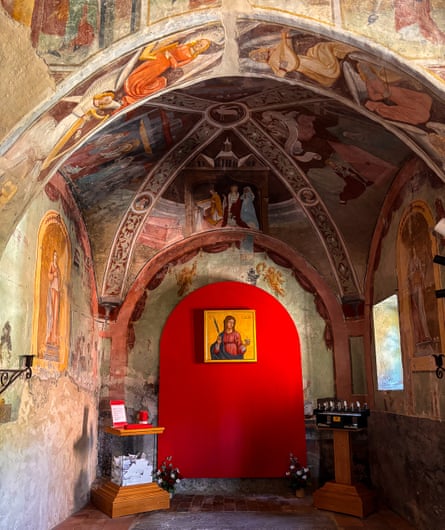 View image in fullscreenFrescoes by Bartolomeo Serra in the chapel of the Santa Lucia delle Vigne, Pinerolo. Photograph: Lavinia Nocelli
View image in fullscreenFrescoes by Bartolomeo Serra in the chapel of the Santa Lucia delle Vigne, Pinerolo. Photograph: Lavinia NocelliThese small churches are maintained by parish volunteers. “These are spaces that promote slow tourism, enabling visitors to discover the area, often through word of mouth,” says Luigi Capello, the head of the local parish youth group and coordinator of pastoral activities. “This project allows us to accompany schools, communities and care homes on visits. But we must not forget the importance of human contact. People can visit the churches independently, yet most of those who return ask to meet one of the volunteers – to hear the story in person.”
The streets of the historic centre of Pinerolo, a municipality in Turin, are enriched by the aromas of bakeries and florists. Inside the cafes, people quickly exchange a greeting, grab an espresso, and leave. Just off the main street is the chapel of Santa Lucia delle Vigne, surrounded by vineyards. Inside are frescoes painted in the 15th century by Bartolomeo Serra and his workshop, depicting four episodes from the saint’s life. Six small wooden cubes serve as benches inside: dim light enters through the window, illuminating Saint Lucia’s face, which looks at the viewer from every side of the nave. The silence is broken only by the narrator’s voice describing the painted scenes. “It’s almost like talking directly to the painter,” says Roberto Billia, a volunteer. “When the door opens, like a miracle, the lights come on and the recording starts. It’s magnificent.”